How To Repair A Torn Ligament
The growing involvement in practise and sports has made genu injuries increasingly mutual.
Arthroscopy allows your surgeon to see into the knee articulation and to address injuries in a more than minimally invasive manner than was traditionally possible. Arthroscopy tin can exist used to care for meniscal and ligament injuries, wearable and tear problems, and to remove loose bodies within the joint. Healing time is typically quite short, scarring minimal, and patients usually go dwelling on the same solar day as their surgery.
Check here if you are looking for information about total knee joint replacement surgery.
These are some of the issues that can be surgically treated with arthroscopic genu surgery:
• Synovitis—inflammation of the synovial membrane
• chondromalacia
• meniscal tears
• ligamentous injuries or tears
• loose bodies
• human knee instability
This article teaches y'all near articulatio genus anatomy, common knee bug and knee arthroscopy. The content and medical illustrations in this commodity are property of Media Partners, Inc. and have been filed with the U.S. Copyright Office.
Healthy Knee Anatomy
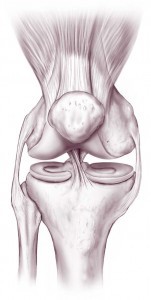
Knowing genu articulation anatomy can help yous to understand your knee trouble better. It can also help you to properly intendance for your knee after your surgery. Proper care often helps shorten your recovery time and improves your surgical outcome.
A articulation is typically formed where two or more than bones encounter. The four bones that meet with ane another to ultimately form the knee joint are the kneecap (patella), thighbone (femur), fibula, and shinbone (tibia).
The parts of the bones that touch each other are covered with articular (or hyaline) cartilage. This cartilage is a shine absorber that helps to protect the bones. The cartilage creates an nigh frictionless surface that allows for painless and complimentary move of the bones against ane some other.
The synovial membrane is a thin layer of tissue that lines the inner aspect of the entire articulatio genus articulation. It produces a substance called synovial fluid. Synovial fluid is a slippery substance that keeps the articulation lubricated and allows for even greater freedom of movement.
The knee joint has two menisci (atypical: meniscus) that sit one height of the tibia. Each meniscus is fabricated up of fibrocartilage, a rubber-like tissue. The menisci act as shock absorbers and also help to improve the stability of the articulatio genus joint. When significant portions of the menisci are damaged or removed, the articular cartilage usually ends up wearing down more than quickly, leading to early arthritis.
Ligaments are rope-like bands of tissue that connect and support the bones of a joint. Several ligaments span the knee joint and act to keep information technology stable.
Tendons are elastic tissues that connect muscles to bones and enable a musculus to movement bone when it contracts. The muscles of the knee and their associated tendons help to farther stabilize the knee joint.
Human knee Problems and Repairs
Knee joint problems can be caused past disease or by injury. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, instability, clicking, communicable, locking, and difficulty walking.
The most mutual knee problems are:
- Torn ligaments
- Meniscal tears
- Loose bodies
- Arthritis or chondromalacia
- Tendonitis
- Bursitis
Torn Ligament
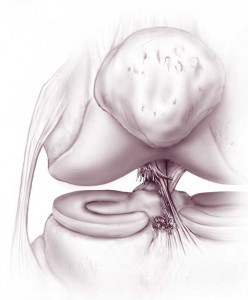
There are many ligaments around the knee that help to stabilize information technology. These include the medial collateral ligament (MCL), lateral collateral ligament (LCL), anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), and the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL).
Sudden first-stop movements and quick changes in direction are common movements during which ligamentous injuries can occur. These types of movements are commonly used in basketball game, football, soccer, and skiing.
Sudden tearing of a ligament may cause pain, swelling or difficulty in walking. More commonly, ligamentous tears may make the genu feel unstable.
Ligamentous injuries range from sprains (stretching or partial violent) to complete tears. Ligament sprains or even some tears are often able to exist treated without any surgery, taking anywhere from four weeks to several months to fully heal. On the other manus, a torn ligament that requires reconstructive surgery can take months to even a year to fully heal.
Some ligamentous injuries (most often tears of the ACL) are associated with meniscal tears.
Ligament Reconstruction
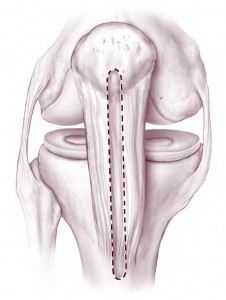
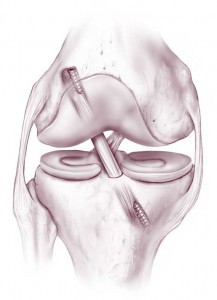
If yous tear a ligament and information technology cannot be treated without surgery, surgical reconstruction of the torn ligament may exist the next step. Typically at this stage, imaging studies including a MRI will accept been ordered to evaluate your injury and to plan for surgery.
Which reconstructive choice volition be best for yous depends on the type of injury y'all accept sustained. Additionally, at that place are numerous means to reconstruct each ligament.
For instance, if you tear your anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), reconstruction (versus repair i.e. tying the two torn ends together) of the ACL is the current standard of care. Your ACL tin exist reconstructed using donor (cadaver) tendon (allograft) or using your own tissue (autograft). At that place are various autograft options available that tin can exist used to reconstruct your ACL (hamstrings, patellar tendon, quadriceps tendon), each with its own pros and cons.
Ultimately, the method used to reconstruct your ACL volition depend on your historic period, activity level, and goals of surgery. This is true of whatsoever ligamentous repair that yous and your surgeon decide to reconstruct (MCL, LCL, PCL).
Finally, ligamentous injuries are often associated with meniscal or cartilage injuries. These are frequently concomitantly addressed at the time of surgery if the surgeon thinks that it is necessary.
Its important to remember that ligaments take a long time to heal. You may have to limit the amount of weight you put on your knee or movement around the knee for several weeks after a ligament reconstruction. You'll probable need crutches to get around initially and your surgeon may enquire that you wear a caryatid to aid support your knee while it heals. At some point, strength and range-of-move exercises will be needed to get your muscles strong enough to support your knee. It can sometimes have up to a year to get dorsum to your normal activities.
Torn Meniscus
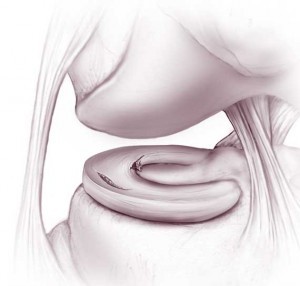
Meniscal injuries can occur afterward forced twisting of the knee (acute meniscal tears). This can happen during sports or fifty-fifty during normal daily activeness. The meniscus also becomes softer with historic period, making it easier to tear. Meniscal tears can also occur in the setting of arthritis (degenerative meniscal tears).
A torn meniscus can cause catching or locking of the articulatio genus, giving way or buckling (instability) of the knee joint, pain or swelling. The size, location, chronicity of the tear as well the presence of any additional injuries will assistance to determine both handling and recovery. If you and your surgeon decide that surgery is the next step, treatment of meniscal tears typically includes either fractional removal or repair. Whether the meniscus is repaired or removed volition depend on many factors including your age, any additional injuries or associated arthritis inside the articulatio genus, and the pattern of tear. Ultimately, the terminal decision to repair or partially remove a meniscus is made by the surgeon at the time of surgery when the injury is directly visualized with the arthroscopic camera. It is only and then that the surgeon can truly understand if the tear is repairable.
It is important to think that non all meniscal tears require surgery i.e. but because somebody says in that location is a meniscal tear on your MRI, doesn't mean that you need surgery. Agreement when surgery is needed will depend on your symptoms, your historic period, whatsoever additional injuries, and your ultimate functional goals. Only you and your orthopedic surgeon can make this decision together.
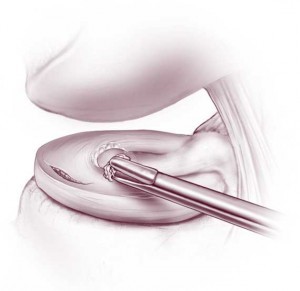
Chondromalacia
Chondromalacia can be caused past overuse or injury to the articular cartilage of the knee joint. This results in softening of the articular cartilage. Information technology most commonly occurs underneath the patella (knee cap) where the patella rubs with the end of the thigh bone (femur). Equally the cartilage softens, it wears away more hands during articulation movements. The cartilage can also just sparse with age. Both of these tin result in loose pieces of cartilage that cause catching or locking of the genu, giving way or buckling of the knee (instability), pain or swelling. Every bit chondromalacia most often involves the patellofemoral compartment (the underside of the patella), the most mutual symptom is forepart of knee pain with walking downwards hills or stairs or pain after prolonged sitting in chairs.
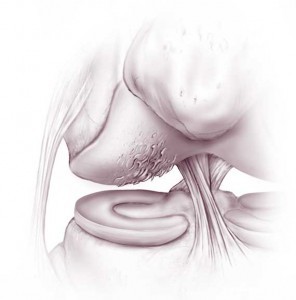
Anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) and physical therapy to stretch and strengthen the hamstrings and quads are the mainstays of treatment for chondromalacia and should virtually always be tried earlier choosing to have surgery. Although uncommon, if medications and physical therapy don't assistance, surgery may be warranted.
Surgical treatment volition depend on how much cartilage is involved and your symptoms. Treatment may include smoothing or shaving down the loose cartilage (chondroplasty) combined with other techniques such as microfracture, etc. Your surgeon will exist hash out with you lot which blazon of surgery volition be most benign for you lot.
Depending on the type of surgery that is performed, postal service-surgical recovery tin take from weeks to months.
Loose Torso (Joint Mouse)
Whatsoever free-floating object in the synovial fluid of the genu is known as a loose trunk or joint mouse. It can be a fragment of bone, cartilage, or meniscus. Information technology can besides be a slice of glass, metal or whatsoever foreign object. A loose body isn't unremarkably noticeable until it lodges somewhere in the joint. Your symptoms tin change depending upon the exact location of the loose body within your articulatio genus. A loose body can cause catching or locking of the knee, giving way or buckling of the knee (instability), hurting or swelling.
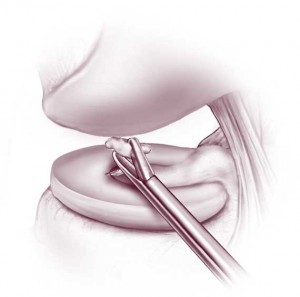
Arthroscopy allows your surgeon to discover the loose body in your knee joint and to remove it.
What is Arthroscopy?
 Now that nosotros've talked well-nigh some of the more than common knee issues that can exist addressed with arthroscopy, let's talk more well-nigh what arthroscopy really is. Arthoscopy allows the surgeon to visualize the inside of the joint and address any bug within information technology.
Now that nosotros've talked well-nigh some of the more than common knee issues that can exist addressed with arthroscopy, let's talk more well-nigh what arthroscopy really is. Arthoscopy allows the surgeon to visualize the inside of the joint and address any bug within information technology.
At the start of an arthroscopic surgery, a small incision is fabricated to enter the genu joint. The arthroscope—a tube with a tiny video camera on the end—is then inserted into the knee joint. The arthroscope has fluid in-menses too as a calorie-free on the end of it. The sterile fluid that flows through the arthroscope and is pumped into the knee expands the joint space and allows your surgeon to come across your joint more than easily. The pressure of this fluid also helps to control haemorrhage.
The inside of your human knee articulation is now viewed on a video monitor. Several more small incisions may exist made around the knee joint allowing for the insertion of other instruments. Commonly used instruments are: forceps, scissors, a blunt hook, a shaver and a burr. These instruments are used to grasp, repair or remove bits of tissue or bone.
Depending on what needs to be done, the surgery itself can last betwixt 30 minutes to several hours. At the conclusion of the surgery, the fluid is drained out. As the surgeon finishes, your incisions are closed with sutures or adhesive strips. Then your knee is bandaged with a pinch bandage to reduce swelling and haemorrhage.
Because only small incisions are made, arthroscopic surgery is an outpatient procedure. This means that you can go habitation the same day that y'all have your surgery.
Getting Ready for Surgery
Since arthroscopic human knee surgery usually is not performed in an emergency setting, y'all will have plenty of time to prepare. Your surgical team will likely give y'all instructions on what to practice in the ii weeks before surgery.
In the weeks / days prior to surgery:
• Tell your surgical team about any and all medications y'all are currently taking — including not-prescription medications, supplements, or herbs
• Y'all volition likely need to stop taking whatsoever medication that makes it harder for your blood to jell. These include: aspirin, plavix, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), naproxen (Naprosyn, Aleve), warfarin (Coumadin), xarelto, pradaxa. Rarely, your doctors may ask you lot to proceed taking these medications effectually the time of surgery. Therefore, it is always best to bank check with both your surgical team and master intendance dr. to see what they recommend.
• Inquire your primary care doctor which of your daily medicines you should take on the mean solar day of surgery.
• If you lot smoke, try to quit. Ask your main intendance doctor for help quitting—simply don't apply a nicotine patch. Smoking (nicotine) tin slow down wound and bone healing and can increase your gamble of developing a wound infection.
• If you lot develop an illness or infection prior to surgery, be sure to call and allow your surgical squad know. If this is the case, sometimes your surgery will have to exist postponed until a later appointment for your rubber. It is ameliorate to know sooner than later so your surgical team can go you rescheduled.
• Let your surgical team know of any abrasions, cuts, or wounds that you may have sustained around your knee. These tin can increase the chance of infection afterwards surgery, and as such, surgery may need to be postponed.
• Get your home set up for your return home. Depending on what blazon of surgery is beingness performed, information technology may be best to set up an area within your domicile where y'all won't have to become up and downwards stairs. Rearrange article of furniture so yous tin can hands get effectually with crutches.
• If possible, strengthen your leg muscles with exercises. In fact, depending on what surgery is planned for you, your surgeon may actually require that you do some therapy prior to surgery to better your range of movement and strengthen your muscles. This volition help with your postal service-operative rehabilitation.
The twenty-four hour period before surgery:
• Shower the night earlier surgery and make sure that your articulatio genus is nice and make clean.
• Do not drink or eat anything later midnight the dark before surgery
On the day of surgery:
• Take whatever medications that your chief care doctor said were okay to have the solar day of surgery with small sips of water
• Go to the hospital or surgery center early. Y'all will probable take to bear witness that yous have brought someone with you that can drive you domicile later surgery
• Wear loose fitting vesture that tin conform a brace or bulky bandage over the knee. Sweat pants or basketball game shorts are good choices.
• If yous were given crutches, cane or a caryatid before surgery, bring this with y'all.
Pre-operative Area
After checking in for surgery, you will go to the pre-operative area. Your claret pressure, heart charge per unit, breathing rate, and temperature are typically closely monitored. You volition likely meet your anesthesiologist here. An intravenous line (IV) may be placed into your arm or paw. The IV allows for medications and fluids to be directly administered into your bloodstream before, during, and later surgery.
• Tell your anesthesiologist if you lot drink more than 1 or 2 drinks of alcohol a day
• Your surgeon will enquire you to sign a surgical consent form if you haven't signed 1 already. By signing the consent grade, yous are saying that you empathize the risks, benefits and possible alternatives to surgery and that you give your permission to become ahead with surgery
Anesthesia
The three types of anesthesia used for arthroscopy are:
• local anesthesia—numbs your human knee expanse
• regional anesthesia—numbs the leg
• general anesthesia—puts you to slumber
Usually, a combination of regional and full general anesthesia are used. Regional anesthesia or a "block" will give you continued pain relief even after you lot wake up. With general anesthesia, the goal is that you are comatose during the surgery and that you lot don't remember the surgery at all.
Recovery Room
At the end of your surgery, you will be taken to the recovery room. You lot will be in recovery until the furnishings of anesthesia accept worn off (usually a few hours), you're past the time point where complications are likely to occur, and you lot're reasonably free of hurting. You can normally have a visitor in the recovery room.
Your claret pressure, heart charge per unit, breathing rate, and temperature are closely monitored. Yous may be given fluids and medicines to assist command pain or nausea associated with general anesthesia. You'll likely have an ice pack on your knee to help keep downwards the swelling. Your surgical leg circulation and sensation are checked past the recovery room nurses.
Discharge – Going Home
Your surgical team decides when you lot're set to exist discharged. Discharge is based on your recovery from anesthesia and whether your pain is adequately controlled. If whatever problems ascend in the recovery room or you need to be watched longer, you may be admitted to the hospital. When you lot're discharged, someone will have to bulldoze you lot habitation.
You may take a big bandage, brace, or water ice pack on your knee that goes dwelling with y'all. A nurse unremarkably reviews mail-operative instructions with you, gets your prescriptions, tells you when to make a follow-up appointment with your surgeon, and what to do if you have any problems when you get home. If you had a nerve block, information technology may take several hours to regain feeling in the affected leg.
Recovery At Dwelling house
Knowing how to care for your knee one time you become home will make a large deviation in your recovery and results. How fast your knee heals depends highly on the surgery performed, your age, your health, your fitness level before surgery, how active you are or want to be, and how much fourth dimension you lot're willing to spend on getting your knee joint back to normal.
Before going home, your surgeon may requite you a set of instructions similar to these:
•Help at home: For the start 24 hours after surgery you should not be left alone. This is if y'all need help or if any unforeseen problems ascend. Remember, you cannot drive immediately subsequently surgery.
• Residual and walking: You may feel groggy for the offset 24-48 hours post-obit surgery. Remainder and requite your body fourth dimension to recover from surgery and anesthesia. Be sure to vesture your brace if your surgeon instructed you to wearable 1. Apply your crutches or other assistive devices, as directed. Exist careful non to trip and fall. Keep your hands free to aid you rest.
• Weight bearing:Your surgical team volition accept explained to you if you can or cannot put weight on your surgical leg.
• Medicine: Have all medications equally prescribed past your surgeon. You may typically resume any of your normal habitation medications unless otherwise directed by your surgical team
• For hurting and swelling: Your knee is likely to feel sore and be bloated for at least a calendar week. Water ice your knee every bit directed. While lying downwards, drag your knee so that it rests above the level of your heart as much as possible. Take hurting medicine as prescribed. (See R.I.C.E. Therapy)
• Crutches: Use assistive devices equally directed by your surgeon.
• Wound care: Keep your wound and bandage dry and clean. With your surgeon's permission, you may remove your bandage a few days after the surgery. At this time, you may typically shower as usual—use a nonslip mat and hand rails when possible until your genu is strong and stable. Do non soak your incisions in a bathtub. Check your incision every 24-hour interval for redness, tenderness, or drainage. It is normal to see some bruising of the wound with some associated swelling of the leg.
• Exercise: Begin a strengthening and range of movement exercise programme as instructed past your surgeon or physical therapist. Don't forget to ice your knee joint later on therapy.
• Return to routine: Return to daily activities and work equally directed by your surgical squad. Return to more vigorous activities once cleared by your surgeon.
When to call your Surgeon:
Telephone call your surgeon to make or confirm a follow-up engagement.
Telephone call your surgical team with whatsoever questions you have about your healing process or if you notice any of the following:
• continued bleeding through the bandage
• A fever over 101.5ºF or if you have shaking chills
• Continued bleeding through the cast
• Persistent swelling, warmth or redness around your human knee
• Tingling in your toes that does not ameliorate, or if they go common cold, discolored or numb
• Persistent or increasing pain, not relieved past your pain medication or with rest
• Hurting, swelling or tenderness in your calf
• Headache, musculus aches or dizziness
• Trouble breathing or chest pain
Phone call 911 if you have chest pain, shortness of breath, or astringent nausea after surgery
Expectations After Arthroscopy
Recovery Time
The amount of time it takes to fully recover after surgery depends on what was done during your surgery. If a "smaller" surgery such as a simple loose body removal was performed, recovery can be as short every bit a matter of weeks. If a large reconstructive surgery was performed, it may take up to a year for your articulatio genus to make a full recovery. The time needed for recovery also depends upon your historic period, your fitness level, and whatsoever other medical bug that yous might have. Afterwards human knee arthroscopy, y'all volition have minor scars on your articulatio genus from the incisions used to perform the surgery.
Frequently Asked Questions After Arthroscopy
- There is blood and drainage from the incisions. Is that OK?A trivial drainage that is watery and articulate or red in color is mutual for the beginning few days following surgery. If the drainage is bright cherry-red or looks like pus and is associated with a fever and/or hurting, call your surgeon right away.
- What if I have a slight fever?Information technology's normal to have a slight fever immediately after surgery. Accept some Tylenol, aspirin, or ibuprofen as directed for the fever. If the fever is in a higher place 101.5F, or persists for more than than a day later on surgery, call your surgical team.
- When can I take a shower or bathroom? Continue your surgical wounds dry for a few days. Typically, you may shower after that and let water run over your wounds. Typically, no scrubbing or soaking of the wounds is allowed for several weeks. Ultimately, confirm these facts with your surgical squad before and later surgery.
- When tin I move effectually?You should be upwards and moving around equally before long as you can after yous recover from anesthesia. To forestall falls, you should non endeavor to walk around unassisted while on narcotic pain medicine. Use assistive devices while on narcotic medications. Ultimately, proficient mobility later surgery volition aid to prevent blood clots and keep your lungs healthy.
- Why is my skin itching? Likely this is a side result of the narcotic pain medication. Narcotic pain medications can make you feel itchy. Unless you develop a rash, hives, or shortness of jiff, you probably are not having an allergic reaction. Y'all tin take an over-the-counter anti-histamine like Claritin or Benadryl to stop the itching. If you are having trouble breathing, telephone call 911.
- Why am I constipated? A side effect of narcotic pain medicines is constipation. This is usually temporary. Also, your lack of activity can add together to the problem. You lot tin can increment the amount of water, fruit, and fiber you swallow. If y'all need information technology, take a stool softener. Potable plenty of h2o. Try to become up and motion effectually as much as you tin can.
- When can I drive?This really depends on the blazon of surgery that was performed. Ask your surgical team when you are able to go back to driving.
- When can I get back to piece of work? This also actually depends on the type of surgery that was performed. Inquire your surgical team when y'all are able to get dorsum to work.
Questions to Ask Your Surgeon About Arthroscopy
• Should I take my daily medicines before surgery?
• How much hurting can I expect after surgery and how will the pain be controlled?
• Will I need crutches or a walker following surgery? For how long? Where can I get these? Should I get them before surgery? Should I bring them to the hospital with me?
• Will I need a brace? For how long? Where do I get ane? Should I become information technology before surgery? Should I bring it to the infirmary with me?
• How soon will I exist able to drive?
• How shortly until I can get back to my normal activities?
• How before long can I go back to piece of work?
• How shortly until I can go back to more strenuous activities like sports or do?
Write downwardly your questions and the answers to these question so you don't forget.
Risks of Having Surgery
Knee joint arthroscopy is generally very prophylactic. However, surgery always has risks. The risks associated with knee joint arthroscopy include:
• Infection of the surgical wounds
• Claret clots in your legs
• Knee joint stiffness
• Failure of repair
Some of the risks associated with surgery are specific to your knee problem and your surgery. Be sure to ask your surgeon which risks are relevant for you.
Notation that the data in this article is purely informative and should never be used in place of the communication of your treating physicians.
Too on Health Pages a guide to Full Knee Replacement Surgery and Recovery
- Knee joint Replacement
- Visit with Orthopedic Surgeon
- Getting Prepare for Surgery
- Making Arrangements for Surgery
- Your Hospital Visit
- Recovery at Home
- Regaining Knee Strength and Motion
- Articulatio genus Replacement Surgery
- Complications of Knee Replacement Surgery
Source: https://www.healthpages.org/surgical-care/knee-arthroscopy/
Posted by: hendersonofectown.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Repair A Torn Ligament"
Post a Comment